golang plugin插件的使用
Go 1.8 为我们提供了一个创建共享库的新工具,称为 Plugins!同时官方文档也提示了:Currently plugins are only supported on Linux and macOS 。其可以应用如下场景:
- 通过plugin我们可以很方便的对于不同功能加载相应的模块并调用相关的模块;
- 也可以针对不同语言(英文、汉语、德语……)加载不同的语言so文件,进行不同的输出;
- 还可以把编译出的文件给不同的编程语言用(如:c/java/python/lua等)。
一、go plugin示例
1、创建插件
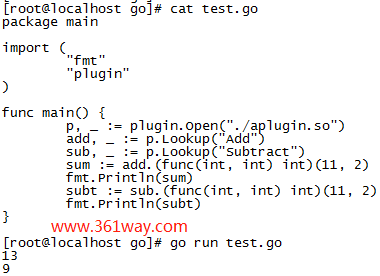
创建一个插件方法aplugin.go:
1package main
2func Add(x, y int) int {
3 return x+y
4}
5func Subtract(x, y int) int {
6 return x-y
7}
构建插件aplugin.so
1go build -buildmode=plugin -o aplugin.so aplugin.go
2、插件调用
不同人类语言调用不同的模块示例,可以参考:https://github.com/vladimirvivien/go-plugin-example 。
二、cshared示例
除了上面提到的buildmode=plugin外,还有一种用法就是 buildmode=c-shared ,使用该参数时会生成出来两个文件,一个.so文件,一个.h头文件 ,使用起来就和使用c 生成的库文件和模块文件一样使用。具体使用如下:
1、awesome.go代码
1package main
2import "C"
3import (
4 "fmt"
5 "math"
6 "sort"
7 "sync"
8)
9var count int
10var mtx sync.Mutex
11//export Add
12func Add(a, b int) int {
13 return a + b
14}
15//export Cosine
16func Cosine(x float64) float64 {
17 return math.Cos(x)
18}
19//export Sort
20func Sort(vals []int) {
21 sort.Ints(vals)
22}
23//export Log
24func Log(msg string) int {
25 mtx.Lock()
26 defer mtx.Unlock()
27 fmt.Println(msg)
28 count++
29 return count
30}
31func main() {}
编译命令如下:
1go build -o awesome.so -buildmode=c-shared awesome.go
2编译后生成如下两个文件:
3awesome.h awesome.h
具体可以使用如下命令查看so文件:
1file awesome.so
2nm awesome.so | grep -e "T Add" -e "T Cosine" -e "T Sort" -e "T Log"
其会输出为shared object文件,并exported 相关对像的symbols 。
2、c语言动态链接调用
1#include
2#include "awesome.h"
3int main() {
4 //Call Add() - passing integer params, interger result
5 GoInt a = 12;
6 GoInt b = 99;
7 printf("awesome.Add(12,99) = %d\n", Add(a, b));
8 //Call Cosine() - passing float param, float returned
9 printf("awesome.Cosine(1) = %f\n", (float)(Cosine(1.0)));
10 //Call Sort() - passing an array pointer
11 GoInt data[6] = {77, 12, 5, 99, 28, 23};
12 GoSlice nums = {data, 6, 6};
13 Sort(nums);
14 printf("awesome.Sort(77,12,5,99,28,23): ");
15 for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++){
16 printf("%d,", ((GoInt *)nums.data)[i]);
17 }
18 printf("\n");
19 //Call Log() - passing string value
20 GoString msg = {"Hello from C!", 13};
21 Log(msg);
22}
编译并调用
1$> gcc -o client client1.c ./awesome.so
2$> ./client
3awesome.Add(12,99) = 111
4awesome.Cosine(1) = 0.540302
5awesome.Sort(77,12,5,99,28,23): 5,12,23,28,77,99,
6Hello from C!
3、c语言动态加载
1#include
2#include
3#include
4// define types needed
5typedef long long go_int;
6typedef double go_float64;
7typedef struct{void *arr; go_int len; go_int cap;} go_slice;
8typedef struct{const char *p; go_int len;} go_str;
9int main(int argc, char **argv) {
10 void *handle;
11 char *error;
12 // use dlopen to load shared object
13 handle = dlopen ("./awesome.so", RTLD_LAZY);
14 if (!handle) {
15 fputs (dlerror(), stderr);
16 exit(1);
17 }
18 // resolve Add symbol and assign to fn ptr
19 go_int (*add)(go_int, go_int) = dlsym(handle, "Add");
20 if ((error = dlerror()) != NULL) {
21 fputs(error, stderr);
22 exit(1);
23 }
24 // call Add()
25 go_int sum = (*add)(12, 99);
26 printf("awesome.Add(12, 99) = %d\n", sum);
27 // resolve Cosine symbol
28 go_float64 (*cosine)(go_float64) = dlsym(handle, "Cosine");
29 if ((error = dlerror()) != NULL) {
30 fputs(error, stderr);
31 exit(1);
32 }
33 // Call Cosine
34 go_float64 cos = (*cosine)(1.0);
35 printf("awesome.Cosine(1) = %f\n", cos);
36 // resolve Sort symbol
37 void (*sort)(go_slice) = dlsym(handle, "Sort");
38 if ((error = dlerror()) != NULL) {
39 fputs(error, stderr);
40 exit(1);
41 }
42 // call Sort
43 go_int data[5] = {44,23,7,66,2};
44 go_slice nums = {data, 5, 5};
45 sort(nums);
46 printf("awesome.Sort(44,23,7,66,2): ");
47 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
48 printf("%d,", ((go_int *)data)[i]);
49 }
50 printf("\n");
51 // resolve Log symbol
52 go_int (*log)(go_str) = dlsym(handle, "Log");
53 if ((error = dlerror()) != NULL) {
54 fputs(error, stderr);
55 exit(1);
56 }
57 // call Log
58 go_str msg = {"Hello from C!", 13};
59 log(msg);
60 // close file handle when done
61 dlclose(handle);
62}
编译执行:
1$> gcc -o client client2.c -ldl
2$> ./client
3awesome.Add(12, 99) = 111
4awesome.Cosine(1) = 0.540302
5awesome.Sort(44,23,7,66,2): 2,7,23,44,66,
6Hello from C!
4、python ctypes 方式调用
1from ctypes import *
2lib = cdll.LoadLibrary("./awesome.so")
3# describe and invoke Add()
4lib.Add.argtypes = [c_longlong, c_longlong]
5lib.Add.restype = c_longlong
6print "awesome.Add(12,99) = %d" % lib.Add(12,99)
7# describe and invoke Cosine()
8lib.Cosine.argtypes = [c_double]
9lib.Cosine.restype = c_double
10print "awesome.Cosine(1) = %f" % lib.Cosine(1)
11# define class GoSlice to map to:
12# C type struct { void *data; GoInt len; GoInt cap; }
13class GoSlice(Structure):
14 _fields_ = [("data", POINTER(c_void_p)), ("len", c_longlong), ("cap", c_longlong)]
15nums = GoSlice((c_void_p * 5)(74, 4, 122, 9, 12), 5, 5)
16# call Sort
17lib.Sort.argtypes = [GoSlice]
18lib.Sort.restype = None
19lib.Sort(nums)
20print "awesome.Sort(74,4,122,9,12) = [",
21for i in range(nums.len):
22 print "%d "% nums.data[i],
23print "]"
24# define class GoString to map:
25# C type struct { const char *p; GoInt n; }
26class GoString(Structure):
27 _fields_ = [("p", c_char_p), ("n", c_longlong)]
28# describe and call Log()
29lib.Log.argtypes = [GoString]
30lib.Log.restype = c_longlong
31msg = GoString(b"Hello Python!", 13)
32print "log id %d"% lib.Log(msg)
执行结果:
1$> python client.py
2awesome.Add(12,99) = 111
3awesome.Cosine(1) = 0.540302
4awesome.Sort(74,4,122,9,12) = [ 4 9 12 74 122 ]
5Hello Python!
5、Python CFFI方式调用
1import sys
2from cffi import FFI
3is_64b = sys.maxsize > 2**32
4ffi = FFI()
5if is_64b: ffi.cdef("typedef long GoInt;\n")
6else: ffi.cdef("typedef int GoInt;\n")
7ffi.cdef("""
8typedef struct {
9 void* data;
10 GoInt len;
11 GoInt cap;
12} GoSlice;
13typedef struct {
14 const char *data;
15 GoInt len;
16} GoString;
17GoInt Add(GoInt a, GoInt b);
18double Cosine(double v);
19void Sort(GoSlice values);
20GoInt Log(GoString str);
21""")
22lib = ffi.dlopen("./awesome.so")
23print("awesome.Add(12,99) = %d" % lib.Add(12,99))
24print("awesome.Cosine(1) = %f" % lib.Cosine(1))
25data = ffi.new("GoInt[]", [74,4,122,9,12])
26nums = ffi.new("GoSlice*", {'data':data, 'len':5, 'cap':5})
27lib.Sort(nums[0])
28print("awesome.Sort(74,4,122,9,12) = %s" % [
29 ffi.cast("GoInt*", nums.data)[i]
30 for i in range(nums.len)])
31data = ffi.new("char[]", b"Hello Python!")
32msg = ffi.new("GoString*", {'data':data, 'len':13})
33print("log id %d" % lib.Log(msg[0]))
6、java调用
1import com.sun.jna.*;
2import java.util.*;
3import java.lang.Long;
4public class Client {
5 public interface Awesome extends Library {
6 // GoSlice class maps to:
7 // C type struct { void *data; GoInt len; GoInt cap; }
8 public class GoSlice extends Structure {
9 public static class ByValue extends GoSlice implements Structure.ByValue {}
10 public Pointer data;
11 public long len;
12 public long cap;
13 protected List getFieldOrder(){
14 return Arrays.asList(new String[]{"data","len","cap"});
15 }
16 }
17 // GoString class maps to:
18 // C type struct { const char *p; GoInt n; }
19 public class GoString extends Structure {
20 public static class ByValue extends GoString implements Structure.ByValue {}
21 public String p;
22 public long n;
23 protected List getFieldOrder(){
24 return Arrays.asList(new String[]{"p","n"});
25 }
26 }
27 // Foreign functions
28 public long Add(long a, long b);
29 public double Cosine(double val);
30 public void Sort(GoSlice.ByValue vals);
31 public long Log(GoString.ByValue str);
32 }
33 static public void main(String argv[]) {
34 Awesome awesome = (Awesome) Native.loadLibrary(
35 "./awesome.so", Awesome.class);
36 System.out.printf("awesome.Add(12, 99) = %s\n", awesome.Add(12, 99));
37 System.out.printf("awesome.Cosine(1.0) = %s\n", awesome.Cosine(1.0));
38 // Call Sort
39 // First, prepare data array
40 long[] nums = new long[]{53,11,5,2,88};
41 Memory arr = new Memory(nums.length * Native.getNativeSize(Long.TYPE));
42 arr.write(0, nums, 0, nums.length);
43 // fill in the GoSlice class for type mapping
44 Awesome.GoSlice.ByValue slice = new Awesome.GoSlice.ByValue();
45 slice.data = arr;
46 slice.len = nums.length;
47 slice.cap = nums.length;
48 awesome.Sort(slice);
49 System.out.print("awesome.Sort(53,11,5,2,88) = [");
50 long[] sorted = slice.data.getLongArray(0,nums.length);
51 for(int i = 0; i < sorted.length; i++){
52 System.out.print(sorted[i] + " ");
53 }
54 System.out.println("]");
55 // Call Log
56 Awesome.GoString.ByValue str = new Awesome.GoString.ByValue();
57 str.p = "Hello Java!";
58 str.n = str.p.length();
59 System.out.printf("msgid %d\n", awesome.Log(str));
60 }
61}
更多示例可以参考:https://github.com/vladimirvivien/go-cshared-examples
三、总结
除了上面提到的示例外,c-shared模式的golang模块还支持nodejs、lua、ruby、Julia等语言的调用。个人理解是大部分语言都是用C开发的,由于golang自身与 c 的亲缘性,所以其生成的模块都是支持其他语言去调用的。
捐赠本站(Donate)
 如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))
如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))
- Author: shisekong
- Link: https://blog.361way.com/go-plugin/5925.html
- License: This work is under a 知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议. Kindly fulfill the requirements of the aforementioned License when adapting or creating a derivative of this work.