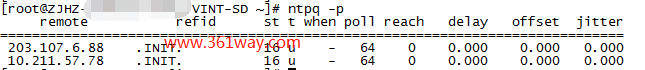配置keys认证的ntp时间服务器
一、 ntp源码安装
因为安全需求的原因,公司要求使用ntp keys认证以防止被用来做反射攻击。需要注意的是,一般系统默认自带的版本会比较老,都存在安全漏洞的,如果OS官方没有推出更新patch的,可以使用源码包编译。具体操作如下:
1yum -y remove ntp ntpdate
2wget http://www.eecis.udel.edu/~ntp/ntp_spool/ntp4/ntp-4.2/ntp-4.2.8p12.tar.gz【会很慢】
3yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ openssl-devel libstdc++* libcap*
4tar -zxvf ntp-4.2.8p12.tar.gz
5cd ntp-4.2.8p12/
6./configure --prefix=/usr --bindir=/usr/sbin --enable-all-clocks --enable-parse-clocks --docdir=/usr/share/doc/ntp-4.2.8p12
7make && make install
8ln -s /usr/local/ntp-4.2.8p12 /usr/local/ntp
二、防火墙配置
rhel6和rhel7会有不同,主要是firewalld与iptables的不同,操作命令如下:
1/sbin/iptables -I INPUT -p udp --dport 123 -j ACCEPT (同时需要/etc/sysconfig/iptables中配置)
2iptables -nL 查询
3firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=123/udp --permanent
4firewall-cmd --reload
5firewall-cmd --query-port=123/udp
6firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports
三、key配置
生成的MD5 keys会在家目录下,通常命名为ntpkey_MD5key_+主机名+随机数字
1[[email protected] ~]# ntp-keygen -M
2[[email protected] ~]# cp ntpkey_md5_361way.com /etc/ntp/keys
3[[email protected] ~]# chmod 600 /etc/ntp/keys
第一列是ID号,后面会用到,一条一个ID号。
如果使用的不是ntp,而是chronyd,也可以使用chrond自带的工具进行key生成。命令如下:
chronyc keygen 3 SHA1
上面的3是id号,可以使用任一数字,后面的sha1是加密算法,也可以使用md5。chronyc生成的ntp-keygen生成的会有不同,ntp-keygen生成的直接是文件,多条,而chronyc根据id只会生成一条,而且不输出到文件,只是在屏幕上打印。chronyc的使用用例如下:
1# generate key id #1 with a 160-bit SHA1 key
2$ chronyc keygen
31 SHA1 HEX:57545218761536EE5FCBCEF67D9F720DE462FB4B
4# generate key id #3 with a 160-bit SHA1 key
5$ chronyc keygen 3 SHA1
63 SHA1 HEX:C47254E85E4FBE1FD2D01FE3BFEA742B32CFB5A2
7# generate key id #16 with a 128-bit SHA256key
8$ chronyc keygen 16 SHA256 128
916 SHA256 HEX:9001F203D6333523E320864C04259B20
10# generate key id #27 with a 512-bit SHA512
11$ chronyc keygen 27 SHA512 512
1227 SHA512 HEX:B08BAAB8DED064D2C2351ED8C9EE5AABE784C80482809C5329187A2BE9D80A0B1E6E18C4164946F6D8E36F1C4A2A966B3B754B1FDE89A0E66FE92CC1E65364E5
四、ntp.conf配置
配置文件内容如下:
1# grep -v ^# /etc/ntp.conf|grep -v ^$
2driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift
3restrict default kod nomodify notrap nopeer noquery notrust
4restrict -6 default kod nomodify notrap nopeer noquery notrust
5restrict 127.0.0.1
6restrict -6 ::1
7restrict 10.211.57.78
8restrict ntp.aliyun.com
9includefile /etc/ntp/crypto/pw
10keys /etc/ntp/keys
11trustedkey 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
12requestkey 8
13controlkey 8
14server ntp.aliyun.com iburst
15server 10.211.57.78 burst iburst
权限的设定主要以 restrict 这个参数来设定,主要的语法为:
restrict IP地址 mask 子网掩码 参数
其中 IP 可以是IP地址,也可以是 default ,default 就是指所有的IP。配置keys认证关键在于notrust参数,该参数的意思是只有trust的才可以访问该ntp服务。如果不加该参数就是表示既允许keys认证的访问,也允许不加keys的访问。
- ignore :关闭所有的 NTP 联机服务
- nomodify:客户端不能更改服务端的时间参数,但是客户端可以通过服务端进行网络校时。
- notrust :客户端除非通过认证,否则该客户端来源将被视为不信任子网
- noquery :不提供客户端的时间查询:用户端不能使用ntpq,ntpc等命令来查询ntp服务器
- notrap :不提供trap远端登陆:拒绝为匹配的主机提供模式 6 控制消息陷阱服务。陷阱服务是 ntpdq 控制消息协议的子系统,用于远程事件日志记录程序。
- nopeer :用于阻止主机尝试与服务器对等,并允许欺诈性服务器控制时钟
- kod : 访问违规时发送 KoD 包。
- restrict -6 表示IPV6地址的权限设置
这里还有一个问题点就是要,如果上面restrict default两条配置并增加notrust后,发现无法和上级对时服务器进行对时了,使用ntpq -p查询,会发现如下情况。
解决该问题比较简单,还是使用restrict参数,放行上级对时服务器,因为这个参数实际上是双向控制,不但对下级进行控制,对上级对时也有控制,试想你默认所有的都不信任的不通过、且nomodify,你和上级对时服务器怎么通信,怎么对时?
1restrict ntp.aliyun.com
可以看上面我的配置文件中,加了下面这样的行。再重启ntp对时服务就好了,这是网上很多资源不对的地方,网上的东西大多是搬运工,不加思索的照搬。restrict 的用法这里给几个示例:
1#掩码地址扩展为255,因此从192.168.0.1-192.168.0.254的服务器都可以使用我们的NTP服务器来同步时间
2restrict 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 notrust nomodify notrap
3#此时表示限制向从192.168.0.1-192.168.0.254这些IP段的服务器提供NTP服务。
4restrict 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 notrust nomodify notrap noquery
5#设置默认策略为允许任何主机进行时间同步
6restrict default ignore
另外还要确保自身有足够的权限,如下两条:
1restrict 127.0.0.1
2restrict -6 ::1
另外还有一个文件/etc/ntp/stpe-tickers会配置上级服务器的地址,这个我觉得是和ntp.conf中的server的配置作用是相同的,这个一般不做修改。在使用server配置中还会遇到server 192.168.7.49 prefer这样的配置文件,其中prefer参数是指定那台上级对时服务器优先级最高。
如果需要同步时间的时候,也把硬件时钟进行同步,可以配置/etc/sysconfig/ntpd文件,在该文件中增加SYNC_HWCLOCK=yes行。
五、客户端配置
可以先使用ntpdate进行验证:
1[root@itohost ntp]# ntpdate 10.212.149.204
203 Mar 10:41:13 ntpdate[9964]: no server suitable for synchronization found
3[root@itohost ntp]# ntpdate -a 4 -k /etc/ntp/keys 10.212.149.204
403 Mar 10:42:52 ntpdate[10156]: adjust time server 10.212.149.204 offset -0.003181 sec
上面可以看出,指定了key的情况下可以进行同步,不指定key的无法进行同步。同样进行ntp.conf配置如下:
1[root@itohost ~]# cat /etc/ntp.conf |grep -v ^#|grep -v ^$
2driftfile /var/lib/ntp/drift
3restrict default kod nomodify notrap nopeer noquery
4restrict -6 default kod nomodify notrap nopeer noquery
5restrict 127.0.0.1
6restrict -6 ::1
7includefile /etc/ntp/crypto/pw
8keys /etc/ntp/keys
9trustedkey 4
10server 10.212.149.204 key 4
这里的keys文件可以是从ntp服务端复制过来的,也可以只写一条记录,比如上面我的是id为4的key进行同步的,里面只写一条id为4的记录也是可以的。
1[root@itohost ~]# ntpq -p
2 remote refid st t when poll reach delay offset jitter
3==============================================================================
4*10.212.149.204 10.211.57.78 4 u - 64 1 1.462 -1.666 0.000
上面的输出结果如下:
- remote – 本机和上层ntp的ip或主机名,“+”表示优先,“*”表示次优先
- refid – 参考上一层ntp主机地址
- st – stratum阶层
- when – 多少秒前曾经同步过时间
- poll – 下次更新在多少秒后
- reach – 已经向上层ntp服务器要求更新的次数
- delay – 网络延迟
- offset – 时间补偿
- jitter – 系统时间与bios时间差
同样,和上层服务器的连接也可以使用ntpstat命令查看。
六、有关chrony
1、ntp.conf与 chrony.conf配置
chrony和ntp的配置方法基本是一样的,只不过chrony对时的效率而好,而且提供的指令在交互式和查询上更精度。chrony服务对应的配置文件为:/etc/chrony.conf ,这里的配置方法和ntp.conf基本可以直接互用。chrony.conf的访问控制相对于ntp比较好用一些,使用的方式如下:
1allow 192.168.2
2allow 10.0.0.0/8
表示允许192.168.2.0/24和10.0.0.0/8两个字网进行访问。
2、chronyc指令
服务启动使用指令是chronyd查询和交互相关的指令主要就是chronyc,具体如下:
1$ chronyc activity
2200 OK
38 sources online //对时服务器个数
40 sources offline
50 sources doing burst (return to online)
60 sources doing burst (return to offline)
70 sources with unknown address
8$ chronyc tracking
9Reference ID : AB42617E (srcf-ntp.stanford.edu)
10Stratum : 2
11Ref time (UTC) : Thu Apr 05 18:27:33 2018
12System time : 0.000669840 seconds slow of NTP time
13Last offset : -0.000506939 seconds
14RMS offset : 0.001261410 seconds
15Frequency : 28.552 ppm slow
16Residual freq : -0.000 ppm
17Skew : 88.846 ppm
18Root delay : 0.031207338 seconds
19Root dispersion : 0.001206590 seconds
20Update interval : 65.2 seconds
21Leap status : Normal
22$ chronyc sources -v
23210 Number of sources = 8
24 .-- Source mode '^' = server, '=' = peer, '#' = local clock.
25 / .- Source state '*' = current synced, '+' = combined , '-' = not combined,
26| / '?' = unreachable, 'x' = time may be in error, '~' = time too variable.
27|| .- xxxx [ yyyy ] +/- zzzz
28|| Reachability register (octal) -. | xxxx = adjusted offset,
29|| Log2(Polling interval) --. | | yyyy = measured offset,
30|| \ | | zzzz = estimated error.
31|| | | \
32MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample
33===============================================================================
34^+ chilipepper.canonical.com 2 7 377 39 +1245us[+1245us] +/- 102ms
35^+ pugot.canonical.com 2 6 377 37 -554us[ -554us] +/- 99ms
36^+ golem.canonical.com 2 6 377 39 -1135us[-1135us] +/- 98ms
37^+ alphyn.canonical.com 2 6 377 44 -87us[ +62us] +/- 74ms
38^* clock.xmission.com 2 6 377 41 -4641ns[ +144us] +/- 41ms
39^+ duffman.whackertech.com 2 6 377 40 -14ms[ -14ms] +/- 89ms
40^+ palpatine.steven-mcdonal> 2 6 177 40 +2565us[+2565us] +/- 46ms
41^+ paladin.latt.net 2 7 377 106 -746us[ -573us] +/- 41ms
42$ chronyc sourcestats -v
43210 Number of sources = 8
44 .- Number of sample points in measurement set.
45 / .- Number of residual runs with same sign.
46 | / .- Length of measurement set (time).
47 | | / .- Est. clock freq error (ppm).
48 | | | / .- Est. error in freq.
49 | | | | / .- Est. offset.
50 | | | | | | On the -.
51 | | | | | | samples. \
52 | | | | | | |
53Name/IP Address NP NR Span Frequency Freq Skew Offset Std Dev
54==============================================================================
55chilipepper.canonical.com 19 9 1170 +1.015 2.938 +166us 1095us
56pugot.canonical.com 7 4 456 -0.639 11.812 +1362us 710us
57golem.canonical.com 9 4 519 -0.315 7.244 +1891us 693us
58alphyn.canonical.com 9 4 518 -0.919 9.460 +1134us 880us
59clock.xmission.com 6 3 390 -1.257 20.127 +1978us 823us
60duffman.whackertech.com 6 3 323 +2.404 25.543 -13ms 680us
61palpatine.steven-mcdonal> 7 3 390 -0.421 15.058 +1776us 742us
62paladin.latt.net 21 14 20m +1.002 2.846 +1085us 1373us
63$ chronyc ntpdata 91.189.94.4 //直接对时了
64Remote address : 91.189.94.4 (5BBD5E04)
65Remote port : 123
66Local address : 192.168.1.203 (C0A801CB)
67Leap status : Normal
68Version : 4
69Mode : Server
70Stratum : 2
71Poll interval : 9 (512 seconds)
72Precision : -23 (0.000000119 seconds)
73Root delay : 0.015991 seconds
74Root dispersion : 0.023285 seconds
75Reference ID : 8CCBCC4D ()
76Reference time : Fri Apr 06 15:55:56 2018
77Offset : +0.004150821 seconds
78Peer delay : 0.144625142 seconds
79Peer dispersion : 0.000000157 seconds
80Response time : 0.000040157 seconds
81Jitter asymmetry: -0.50
82NTP tests : 111 111 1111
83Interleaved : No
84Authenticated : No
85TX timestamping : Daemon
86RX timestamping : Kernel
87Total TX : 38
88Total RX : 38
89Total valid RX : 38
90$ chronyc clients
91Hostname NTP Drop Int IntL Last Cmd Drop Int Last
92===============================================================================
93viper.maas 390 0 0 - 0 0 0 - -
94localhost 0 0 - - - 1 0 - 2
认证同步还可以进行交互式操作,如下:
1chronyc> authhash SHA1
2chronyc> password HEX:A6CFC50C9C93AB6E5A19754C246242FC5471BCDF
3200 OK
而且可以查询是否使用的keys认证:
1$ chronyc ntpdata 192.168.2.12 | grep Authenticated
2Authenticated : Yes
捐赠本站(Donate)
 如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))
如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))
- Author: shisekong
- Link: https://blog.361way.com/ntp-chrony-keys/6273.html
- License: This work is under a 知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议. Kindly fulfill the requirements of the aforementioned License when adapting or creating a derivative of this work.