python threading之Condition
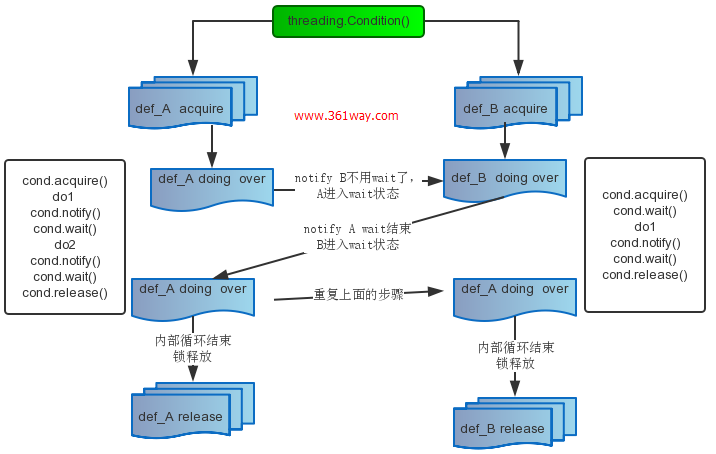
Python提供的Condition对象提供了对复杂线程同步问题的支持。Condition被称为条件变量,除了提供与Lock类似的acquire和release方法外,还提供了wait和notify方法。线程首先acquire一个条件变量,然后判断一些条件。如果条件不满足则wait;如果条件满足,进行一些处理改变条件后,通过notify方法通知其他线程,其他处于wait状态的线程接到通知后会重新判断条件。不断的重复这一过程,从而解决复杂的同步问题。
除了上面画的acquire方法、 release方法、notify方法、wait方法外还有notifyAll方法,不过notifyAll方法不常用。
51cto博客上我看到一篇博文中,形象的以二人对话 (生产者-消费者模)来解释上面的具体理论。
其中空格哥对应原理图中的A函数 ,西米对应的B 函数,每句话是doing操作,空格哥未“doing” 前,西米需要一直等待。最后,你来我往,直到最后都release掉,对话结束。由于代码太长,我给个精简版的,模拟上面的对话:
1#coding:utf-8
2#---- Condition
3#---- 捉迷藏的游戏
4import threading, time
5class Hider(threading.Thread):
6 def __init__(self, cond, name):
7 super(Hider, self).__init__()
8 self.cond = cond
9 self.name = name
10 def run(self):
11 time.sleep(1) #确保先运行Seeker中的方法
12 self.cond.acquire() #b
13 print self.name + ': 我已经把眼睛蒙上了'
14 self.cond.notify()
15 self.cond.wait() #c
16 #f
17 print self.name + ': 我找到你了 ~_~'
18 self.cond.notify()
19 self.cond.release()
20 #g
21 print self.name + ': 我赢了' #h
22class Seeker(threading.Thread):
23 def __init__(self, cond, name):
24 super(Seeker, self).__init__()
25 self.cond = cond
26 self.name = name
27 def run(self):
28 self.cond.acquire()
29 self.cond.wait() #a #释放对琐的占用,同时线程挂起在这里,直到被notify并重新占有琐。
30 #d
31 print self.name + ': 我已经藏好了,你快来找我吧'
32 self.cond.notify()
33 self.cond.wait() #e
34 #h
35 self.cond.release()
36 print self.name + ': 被你找到了,哎~~~'
37cond = threading.Condition()
38seeker = Seeker(cond, 'seeker')
39hider = Hider(cond, 'hider')
40seeker.start()
41hider.start()
执行结果如下:
1[root@361way condition]# python con3.py
2hider: 我已经把眼睛蒙上了
3seeker: 我已经藏好了,你快来找我吧
4hider: 我找到你了 ~_~
5seeker: 被你找到了,哎~~~
6hider: 我赢了
便于对比,这里再给一个无限循环的例子。经典的生产者与消费者问题:假设有一群生产者(Producer)和一群消费者(Consumer)通过一个市场来交互产品。生产者的”策略“是如果市场上剩余的产品少于1000个,那么就生产100个产品放到市场上;而消费者的”策略“是如果市场上剩余产品的数量多余100个,那么就消费3个产品。用Condition解决生产者与消费者问题的代码如下:
1import threading
2import time
3class Producer(threading.Thread):
4 def run(self):
5 global count
6 while True:
7 if con.acquire():
8 if count > 1000:
9 con.wait()
10 else:
11 count = count+100
12 msg = self.name+' produce 100, count=' + str(count)
13 print msg
14 con.notify()
15 con.release()
16 time.sleep(1)
17class Consumer(threading.Thread):
18 def run(self):
19 global count
20 while True:
21 if con.acquire():
22 if count < 100:
23 con.wait()
24 else:
25 count = count-3
26 msg = self.name+' consume 3, count='+str(count)
27 print msg
28 con.notify()
29 con.release()
30 time.sleep(1)
31count = 500
32con = threading.Condition()
33def test():
34 for i in range(2):
35 p = Producer()
36 p.start()
37 for i in range(5):
38 c = Consumer()
39 c.start()
40if __name__ == '__main__':
41 test()
捐赠本站(Donate)
 如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))
如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))
- Author: shisekong
- Link: https://blog.361way.com/thread-condition/4621.html
- License: This work is under a 知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议. Kindly fulfill the requirements of the aforementioned License when adapting or creating a derivative of this work.