Huaweicloud CCE helm install Bitnami PostgreSQL
Bitnami is a company that provides pre-packaged software stacks for popular open source applications(Belong the VMware Sub-company).
Here are some of the benefits of using Bitnami stacks:
- Easy to install and use
- Regularly updated with security patches and bug fixes
- Available for a variety of platforms
- Wide range of applications available
- Community support
So we are install the postgresql to Huaweicloud CCE platform (A famous k8s commercial platform ) today .
1. Install the helm3
Note: we need install the newest version from helm official website , we cannot use the huaweicloud official document (the website offer the old helm version , there will be have the error Error: parse error at (postgresql/templates/_helpers.tpl:164): unclosed action)
Install helm command like this:
1curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/helm/master/scripts/get-helm-3 > get_helm.sh
2chmod 700 get_helm.sh
3./get_helm.sh
4
5# or one line command like this:
6curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3 | bash
2. helm3 install PostgreSQL
The new helm use oci install the application , let’s try use the below command:
1helm install my-release oci://registry-1.docker.io/bitnamicharts/postgresql
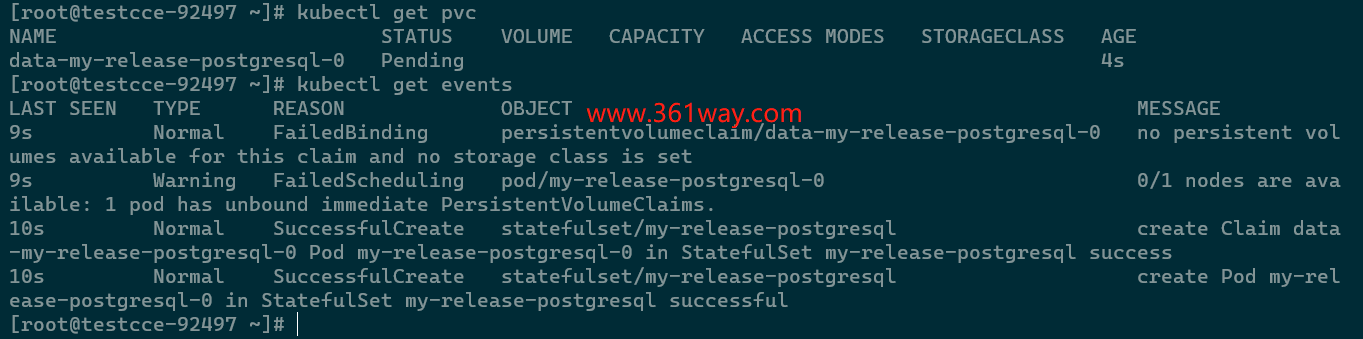
But when we check the install result, we found the application install failed. Use the command kubectl get PVC and kubectl get events get the detail information, we know the failed reason is there didn’t have the available PVC and PV for use.
3. helm3 add the parameters
We can checked the parameters in the artifacthub. some parameters like this:
1--set primary.persistence.existingClaim=postgres-pvc \
2--set volumePermissions.enabled=true \
3--set global.postgresql.auth.postgresPassword={your-postgres-admin-password} \
4--set global.postgresql.auth.username={your-postgres-username} \
5--set global.postgresql.auth.password={your-postgres-password} \
6--set global.postgresql.auth.database={your-postgres-database}
And we can also use the helm show command see the details values setting.
1 helm show values oci://registry-1.docker.io/bitnamicharts/postgresql > values.yaml
We can edit values.yaml file, use helm install pgdatabase oci://registry-1.docker.io/bitnamicharts/postgresql -f values.yaml command install also.
4. Start from begins
a. Create dynamic PVC
Edit a dynamic PVC yaml file:
1apiVersion: v1
2kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
3metadata:
4 name: pg-data-pvc
5 namespace: default
6 labels:
7 app: pg-data-pvc
8spec:
9 storageClassName: csi-disk
10 accessModes:
11 - ReadWriteOnce
12 resources:
13 requests:
14 storage: 8Gi
Create PVC and PV:
1kubectl apply -f pg-pvc.yaml
b. Install postgresql use helm
1helm install pgdatabase oci://registry-1.docker.io/bitnamicharts/postgresql \
2--set primary.persistence.existingClaim=pg-data-pvc \
3--set volumePermissions.enabled=true \
4--set global.postgresql.auth.postgresPassword={your-postgres-admin-password} \
5--set global.postgresql.auth.username={your-postgres-username} \
6--set global.postgresql.auth.password={your-postgres-password} \
7--set global.postgresql.auth.database={your-postgres-database}
c. Check the install result
1[root@testcce-92497 ~]# kubectl apply -f pg-pvc.yaml
2persistentvolumeclaim/pg-data-pvc created
3
4[root@testcce-92497 ~]# helm install pgdatabase oci://registry-1.docker.io/bitnamicharts/postgresql \
5--set primary.persistence.existingClaim=pg-data-pvc \
6--set volumePermissions.enabled=true \
7--set global.postgresql.auth.postgresPassword=mypgpasswd
8
9[root@testcce-92497 ~]# kubectl get pods
10NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
11pgdatabase-postgresql-0 1/1 Running 0 35s
12
13[root@testcce-92497 ~]# kubectl exec -it pgdatabase-postgresql-0 -- /bin/bash
14Defaulted container "postgresql" out of: postgresql, init-chmod-data (init)
15I have no name!@pgdatabase-postgresql-0:/$ PGPASSWORD="$POSTGRES_PASSWORD" psql --host 127.0.0.1 -U postgres -d postgres -p 5432
16psql (15.3)
17Type "help" for help.
18
19postgres=# \l
20 List of databases
21Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | ICU Locale | Locale Provider | Access privileges
22-----------+----------+----------+-------------+-------------+------------+-----------------+------------------
23postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | libc |
24template0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | libc | =c/postgres+ |
25template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | | libc | =c/postgres + |
26(3 rows)
5. Create master/standby Postgresql
This helm charts support master/standby architecture. primary.standby.enabled set true is open this function, and set the readReplicas.persistence.existingClaim for slave node persistence disk, set the architecture to replication.
a. create PersistentVolumeClaim for master/standby
1[root@testcce-92497 pg]# cat primary.yaml
2apiVersion: v1
3kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
4metadata:
5 name: data-pgdatabase-postgresql-primary-0
6 namespace: default
7 labels:
8 app: data-pgdatabase-postgresql-primary-0
9spec:
10 storageClassName: csi-disk
11 accessModes:
12 - ReadWriteOnce
13 resources:
14 requests:
15 storage: 8Gi
16[root@testcce-92497 pg]# cat read-pvc.yaml
17apiVersion: v1
18kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
19metadata:
20 name: data-pgdatabase-postgresql-read-0
21 namespace: default
22 labels:
23 app: data-pgdatabase-postgresql-read-0
24spec:
25 storageClassName: csi-disk
26 accessModes:
27 - ReadWriteOnce
28 resources:
29 requests:
30 storage: 8Gi
31
32[root@testcce-92497 pg]# kubectl apply -f primary.yaml -f read-pvc.yaml
33persistentvolumeclaim/data-pgdatabase-postgresql-primary-0 created
34persistentvolumeclaim/data-pgdatabase-postgresql-read-0 created
b. create master/standby architecture
use the blow command for create the postgresql:
1helm install pgdatabase oci://registry-1.docker.io/bitnamicharts/postgresql \
2--set primary.persistence.existingClaim=data-pgdatabase-postgresql-primary-0 \
3--set volumePermissions.enabled=true \
4--set global.postgresql.auth.postgresPassword=mypgpasswd \
5--set architecture=replication \
6--set readReplicas.persistence.existingClaim=data-pgdatabase-postgresql-read-0
c. verify the result
Ensure the pods,statefulset,service is successful:
1[root@testcce-92497 ~]# kubectl get pods
2NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
3pgdatabase-postgresql-primary-0 1/1 Running 0 14m
4pgdatabase-postgresql-read-0 1/1 Running 0 14m
5[root@testcce-92497 ~]# kubectl get svc
6NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
7kubernetes ClusterIP 10.247.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 2d6h
8pgdatabase-postgresql-primary ClusterIP 10.247.237.128 <none> 5432/TCP 7m6s
9pgdatabase-postgresql-primary-hl ClusterIP None <none> 5432/TCP 7m6s
10pgdatabase-postgresql-read ClusterIP 10.247.162.25 <none> 5432/TCP 7m6s
11pgdatabase-postgresql-read-hl ClusterIP None <none> 5432/TCP 7m6s
12[root@testcce-92497 ~]# kubectl get sfs
13error: the server doesn't have a resource type "sfs"
14[root@testcce-92497 ~]# kubectl get sts
15NAME READY AGE
16pgdatabase-postgresql-primary 1/1 7m23s
17pgdatabase-postgresql-read 1/1 7m23s
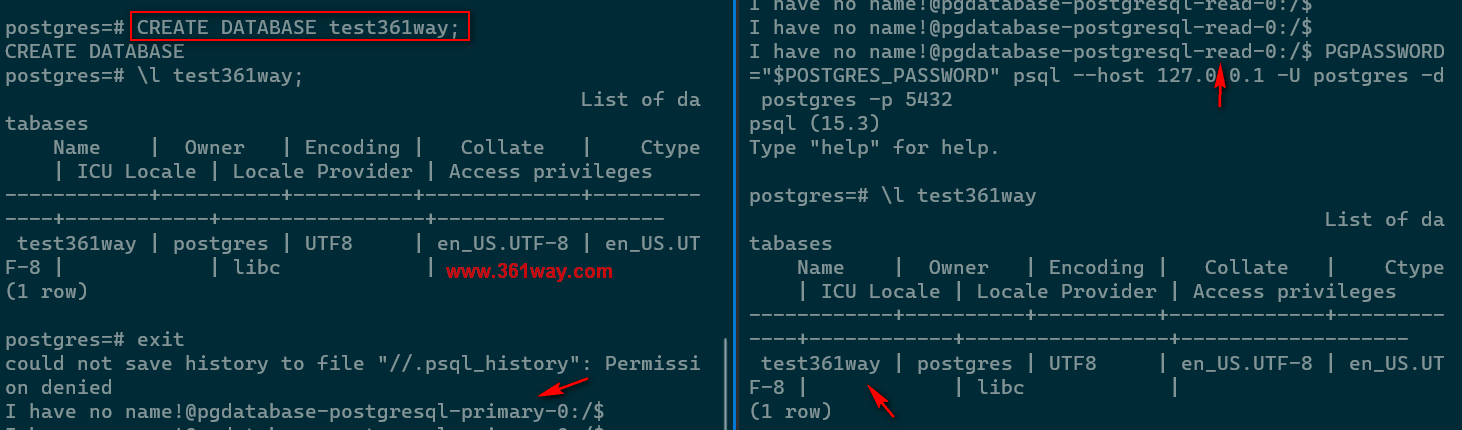
create a test database in master node, check in the standy read database.
捐赠本站(Donate)
 如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))
如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))
- Author: shisekong
- Link: https://blog.361way.com/huaweicloud-cce-helm-install-pgsql/8561.html
- License: This work is under a 知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议. Kindly fulfill the requirements of the aforementioned License when adapting or creating a derivative of this work.