从kubectl top看K8S监控原理
一、前言
kubectl top 可以很方便地查看node、pod 的实时资源使用情况:如CPU、内存。这篇文章会介绍其数据链路和实现原理,同时借 kubectl top 阐述 k8s 中的监控体系,窥一斑而知全豹。最后会解释常见的一些问题:
- kubectl top 为什么会报错?
- kubectl top node 怎么计算,和节点上直接 top 有什么区别?
- kubectl top pod 怎么计算,包含 pause 吗?
- kubectl top pod 和exec 进入 pod 后看到的 top 不一样?
- kubectl top pod 和 docker stats得到的值为什么不同?
以下命令的运行环境为:
- k8s 1.8
- k8s 1.13
二、使用
kubectl top 是基础命令,但是需要部署配套的组件才能获取到监控值
- 1.8以下:部署 heapter
- 1.8以上:部署 metric-server
kubectl top node: 查看node的使用情况
1[root@testcce-38725 ~]# kubectl top node
2NAME CPU(cores) CPU% MEMORY(bytes) MEMORY%
3192.168.0.78 74m 0% 934Mi 6%
4[root@testcce-38725 ~]# kubectl top node 192.168.0.78
5NAME CPU(cores) CPU% MEMORY(bytes) MEMORY%
6192.168.0.78 74m 0% 934Mi 6%
kubectl top pod: 查看 pod 的使用情况
1[root@testcce-38725 ~]# kubectl top pod
2NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
3nginx-84f87fccc4-g8h24 0m 5Mi
4nginx-84f87fccc4-pxnb9 2m 5Mi
5[root@testcce-38725 ~]# kubectl top pod nginx-84f87fccc4-pxnb9
6NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
7nginx-84f87fccc4-pxnb9 2m 5Mi
8[root@testcce-38725 ~]# kubectl top pod nginx-84f87fccc4-pxnb9 --containers
9POD NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
10nginx-84f87fccc4-pxnb9 container-0 0m 5Mi
不指定pod 名称,则显示命名空间下所有 pod,–containers可以显示 pod 内所有的container。
指标含义:
- 和 k8s中 的 request、limit 一致,CPU单位100m=0.1 内存单位1Mi=1024Ki
- pod 的内存值是其实际使用量,也是做 limit 限制时判断 oom 的依据。pod的使用量等于其所有业务容器的总和,不包括 pause 容器,值等于 cadvisr中的
container_memory_working_set_bytes指标 - node 的值并不等于该 node 上所有 pod 值的总和,也不等于直接在机器上运行 top 或 free 看到的值
三、实现原理
3.1 数据链路
kubectl top、 k8s dashboard 以及 HPA 等调度组件使用的数据是一样,数据链路如下:
使用 heapster 时:apiserver 会直接将 metric 请求通过 proxy 的方式转发给集群内的 hepaster 服务。
而使用 metrics-server 时:apiserver 是通过 /apis/metrics.k8s.io/ 的地址访问 metric
3.2 metric api
可以发现,heapster 使用的是 proxy 转发,而 metric-server 和普通 pod都是使用 api/xx 的资源接口,heapster采用的这种 proxy 方式是有问题的:
- proxy 只是代理请求,一般用于问题排查,不够稳定,且版本不可控
- heapster 的接口不能像 apiserver 一样有完整的鉴权以及 client 集成,两边都维护的话代价高,如 generic apiserver
- pod 的监控数据是核心指标(HPA调度),应该和 pod 本身拥有同等地位,即 metric 应该作为一种资源存在,如 metrics.k8s.io 的形式,称之为 Metric Api
于是官方从 1.8 版本开始逐步废弃 heapster,并提出了上边 Metric api 的概念,而 metrics-server 就是这种概念下官方的一种实现,用于从 kubelet获取指标,替换掉之前的 heapster。
3.3 kube-aggregator
有了 metrics-server 组件,采集到了需要的数据,也暴露了接口,但走到这一步和 heapster 其实没有区别,最关键的一步就是如何将打到 apiserver的 /apis/metrics.k8s.io 请求转发给 metrics-server 组件?解决方案就是:kube-aggregator。kube-aggregator 是对 apiserver 的有力扩展,它允许 k8s 的开发人员编写一个自己的服务,并把这个服务注册到 k8s 的 api 里面,即扩展 API,metric-server 其实在 1.7版本就已经完成了,只是在等 kube-aggregator 的出现。kube-aggregator 是 apiserver 中的实现,有些 k8s 版本默认没开启,你可以加上这些配置来开启,他的核心功能是动态注册、发现汇总、安全代理。
如 metric-server 注册 pod 和 node 时:
3.4 监控体系
在提出 metric api 的概念时,官方也提出了新的监控体系,监控资源被分为了2种:
- Core metrics(核心指标):从 Kubelet、cAdvisor 等获取度量数据,再由metrics-server 提供给 Dashboard、HPA 控制器等使用。
- Custom Metrics(自定义指标):由 Prometheus Adapter 提供 API custom.metrics.k8s.io,由此可支持任意Prometheus采集到的指标。
核心指标只包含 node 和 pod 的 cpu、内存等,一般来说,核心指标作 HPA 已经足够,但如果想根据自定义指标:如请求 qps/5xx 错误数来实现 HPA,就需要使用自定义指标了。目前 Kubernetes 中自定义指标一般由 Prometheus 来提供,再利用 k8s-prometheus-adpater 聚合到 apiserver,实现和核心指标同样的效果。
3.5 kubelet
前面提到,无论是 heapster 还是 metric-server,都只是数据的中转和聚合,两者都是调用的 kubelet 的 api 接口获取的数据,而 kubelet 代码中实际采集指标的是 cadvisor 模块,你可以在 node 节点访问 10255 端口(1.11版本过后是10250端口)获取监控数据:
- Kubelet Summary metrics: 127.0.0.1:10255/metrics,暴露 node、pod 汇总数据
- Cadvisor metrics: 127.0.0.1:10255/metrics/cadvisor,暴露 container 维度数据
示例,容器的内存使用量:
Kubelet 虽然提供了 metric 接口,但实际监控逻辑由内置的 cAdvisor 模块负责,演变过程如下:
- 从k8s 1.6开始,kubernetes 将 cAdvisor 开始集成在kubelet中,不需要单独配置
- 从k8s 1.7开始,Kubelet metrics API 不再包含 cadvisor metrics,而是提供了一个独立的 API 接口来做汇总
- 从 k8s 1.12 开始,cadvisor 监听的端口在k8s中被删除,所有监控数据统一由 Kubelet 的 API 提供
到这里为止,k8s 范围内的监控体系就结束了。
3.6 cadvisor
cadvisor 由谷歌开源,使用 Go 开发,cadvisor 不仅可以搜集一台机器上所有运行的容器信息,包括 CPU 使用情况、内存使用情况、网络吞吐量及文件系统使用情况,还提供基础查询界面和 http 接口,方便其他组件进行数据抓取。在K8S 中集成在 Kubelet 里作为默认启动项,k8s 官方标配。cadvisor 拿到的数据结构示例:
1type MemoryStats struct {
2 // Current memory usage, this includes all memory regardless of when it was
3 // accessed.
4 // Units: Bytes.
5 Usage uint64 `json:"usage"`
6
7 // Maximum memory usage recorded.
8 // Units: Bytes.
9 MaxUsage uint64 `json:"max_usage"`
10
11 // Number of bytes of page cache memory.
12 // Units: Bytes.
13 Cache uint64 `json:"cache"`
14
15 // The amount of anonymous and swap cache memory (includes transparent
16 // hugepages).
17 // Units: Bytes.
18 RSS uint64 `json:"rss"`
19
20 // The amount of swap currently used by the processes in this cgroup
21 // Units: Bytes.
22 Swap uint64 `json:"swap"`
23
24 // The amount of memory used for mapped files (includes tmpfs/shmem)
25 MappedFile uint64 `json:"mapped_file"`
26
27 // The amount of working set memory, this includes recently accessed memory,
28 // dirty memory, and kernel memory. Working set is
注:上面的是cadvisor v1里的源码,通过该链接也可以查看v2部分的源码。
核心逻辑是通过 new 出来的 memoryStorage 以及 sysfs 实例,创建一个manager 实例,manager 的 interface 中定义了许多用于获取容器和 machine 信息的函数。
1type Manager interface {
2 // Start the manager. Calling other manager methods before this returns
3 // may produce undefined behavior.
4 Start() error
5
6 // Stops the manager.
7 Stop() error
8
9 // information about a container.
10 GetContainerInfo(containerName string, query *info.ContainerInfoRequest) (*info.ContainerInfo, error)
11
12 // Get V2 information about a container.
13 // Recursive (subcontainer) requests are best-effort, and may return a partial result alongside an
14 // error in the partial failure case.
15 GetContainerInfoV2(containerName string, options v2.RequestOptions) (map[string]v2.ContainerInfo, error)
16
17 // Get information about all subcontainers of the specified container (includes self).
18 SubcontainersInfo(containerName string, query *info.ContainerInfoRequest) ([]*info.ContainerInfo, error)
19
20 // Gets all the Docker containers. Return is a map from full container name to ContainerInfo.
21 AllDockerContainers(query *info.ContainerInfoRequest) (map[string]info.ContainerInfo, error)
22
23 // Gets information about a specific Docker container. The specified name is within the Docker namespace.
24 DockerContainer(dockerName string, query *info.ContainerInfoRequest) (info.ContainerInfo, error)
25
26 // Gets spec for all containers based on request options.
27 GetContainerSpec(containerName string, options v2.RequestOptions) (map[string]v2.ContainerSpec, error)
28
29 // Gets summary stats for all containers based on request options.
30 GetDerivedStats(containerName string, options v2.RequestOptions) (map[string]v2.DerivedStats, error)
31
32 // Get info for all requested containers based on the request options.
33 GetRequestedContainersInfo(containerName string, options v2.RequestOptions) (map[string]*info.ContainerInfo, error)
34
35 // Returns true if the named container exists.
36 Exists(containerName string) bool
37
38 // Get information about the machine.
39 GetMachineInfo() (*info.MachineInfo, error)
40……
这部分源码参看:cadvisor manager源码
cadvisor的指标解读:cgroup-v1(https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/cgroup-v1/memory.txt)
cadvisor 获取指标时实际调用的是 runc/libcontainer 库,而 libcontainer 是对 cgroup 文件 的封装,即 cadvsior 也只是个转发者,它的数据来自于cgroup 文件。
3.7 cgroup
cgroup 文件中的值是监控数据的最终来源,如
- mem usage 的值,来自于
/sys/fs/cgroup/memory/docker/[containerId]/memory.usage_in_bytes - 如果没限制内存,Limit=machine_mem,否则来自于
/sys/fs/cgroup/memory/docker/[id]/memory.limit_in_bytes - 内存使用率=memory.usage_in_bytes/memory.limit_in_bytes
一般情况下,cgroup文件夹下的内容包括CPU、内存、磁盘、网络等信息:
如 memory 下的几个常用的指标含义:
1memory.usage_in_bytes # show current usage for memory
2 (See 5.5 for details)
3 memory.memsw.usage_in_bytes # show current usage for memory+Swap
4 (See 5.5 for details)
5 memory.limit_in_bytes # set/show limit of memory usage
6 memory.memsw.limit_in_bytes # set/show limit of memory+Swap usage
7 memory.failcnt # show the number of memory usage hits limits
8 memory.memsw.failcnt # show the number of memory+Swap hits limits
9 memory.max_usage_in_bytes # show max memory usage recorded
10 memory.memsw.max_usage_in_bytes # show max memory+Swap usage recorded
11 memory.soft_limit_in_bytes # set/show soft limit of memory usage
12 memory.stat # show various statistics
memory.stat 中的信息是最全的:
1cache - # of bytes of page cache memory.
2rss - # of bytes of anonymous and swap cache memory (includes transparent hugepages).
3rss_huge - # of bytes of anonymous transparent hugepages.
4mapped_file - # of bytes of mapped file (includes tmpfs/shmem)
5pgpgin - # of charging events to the memory cgroup. The charging
6 event happens each time a page is accounted as either mapped
7 anon page(RSS) or cache page(Page Cache) to the cgroup.
8pgpgout - # of uncharging events to the memory cgroup. The uncharging
9 event happens each time a page is unaccounted from the cgroup.
10swap - # of bytes of swap usage
11dirty - # of bytes that are waiting to get written back to the disk.
12writeback - # of bytes of file/anon cache that are queued for syncing to disk.
13inactive_anon - # of bytes of anonymous and swap cache memory on inactive LRU list.
14active_anon - # of bytes of anonymous and swap cache memory on active LRU list.
15inactive_file - # of bytes of file-backed memory on inactive LRU list.
16active_file - # of bytes of file-backed memory on active LRU list.
17unevictable - # of bytes of memory that cannot be reclaimed (mlocked etc).
原理到这里结束,这里解释下最开始的 kubectl top 的几个问题:
四、问题
一般情况下 top 报错有以下几种,可以 kubectl top pod -v=10看到具体的调用日志:
- 没有部署 heapster 或者 metric-server,或者 pod 运行异常,可以排查对应 pod 日志
- 要看的 pod 刚刚建出来,还没来得及采集指标,报 not found 错误,默认 1 分钟
- 以上两种都不是,可以检查下 kubelet 的 10255 端口是否开放,默认情况下会使用这个只读端口获取指标,也可以在 heapster 或 metric-server 的配置中增加证书,换成 10250 认证端口
4.2 kubectl top pod 内存怎么计算,包含 pause容器吗
每次启动 pod,都会有一个 pause 容器,既然是容器就一定有资源消耗(一般在 2-3M 的内存),cgroup 文件中,业务容器和 pause 容器都在同一个 pod的文件夹下。
但 cadvisor 在查询 pod 的内存使用量时,是先获取了 pod 下的container列表,再逐个获取container的内存占用,不过这里的 container 列表并没有包含 pause,因此最终 top pod 的结果也不包含 pause 容器pod 的内存使用量计算kubectl top pod 得到的内存使用量,并不是 cadvisor 中的 container_memory_usage_bytes,而是 container_memory_working_set_bytes,计算方式为:
- container_memory_usage_bytes = container_memory_rss + container_memory_cache + kernel memory
- container_memory_working_set_bytes = container_memory_usage_bytes – total_inactive_file(未激活的匿名缓存页)
container_memory_working_set_bytes 是容器真实使用的内存量,也是 limit限制时的 oom 判断依据。cadvisor 中的 container_memory_usage_bytes 对应 cgroup 中的 memory.usage_in_bytes 文件,但 container_memory_working_set_bytes 并没有具体的文件,他的计算逻辑在 cadvisor 的代码中,如下:
1func (sp *summaryProviderImpl) GetSystemContainersCPUAndMemoryStats(nodeConfig cm.NodeConfig, podStats []statsapi.PodStats, updateStats bool) (stats []statsapi.ContainerStats) {
2 systemContainers := map[string]struct {
3 name string
4 forceStatsUpdate bool
5 startTime metav1.Time
6 }{
7 statsapi.SystemContainerKubelet: {name: nodeConfig.KubeletCgroupsName, forceStatsUpdate: false, startTime: sp.kubeletCreationTime},
8 statsapi.SystemContainerRuntime: {name: nodeConfig.RuntimeCgroupsName, forceStatsUpdate: false},
9 statsapi.SystemContainerMisc: {name: nodeConfig.SystemCgroupsName, forceStatsUpdate: false},
10 statsapi.SystemContainerPods: {name: sp.provider.GetPodCgroupRoot(), forceStatsUpdate: updateStats},
11 }
12 for sys, cont := range systemContainers {
13 // skip if cgroup name is undefined (not all system containers are required)
14 if cont.name == "" {
15 continue
16 }
17 s, err := sp.provider.GetCgroupCPUAndMemoryStats(cont.name, cont.forceStatsUpdate)
18 if err != nil {
19 klog.ErrorS(err, "Failed to get system container stats", "containerName", cont.name)
20 continue
21 }
22 s.Name = sys
23
24 // if we know the start time of a system container, use that instead of the start time provided by cAdvisor
25 if !cont.startTime.IsZero() {
26 s.StartTime = cont.startTime
27 }
28 stats = append(stats, *s)
29 }
同理,node 的内存使用量也是 container_memory_working_set_bytes。
4.3 kubectl top node 怎么计算,和节点上直接 top 有什么区别
kubectl top node 得到的 cpu 和内存值,并不是节点上所有 pod 的总和,不要直接相加。top node 是机器上 cgroup 根目录下的汇总统计。
1workingSet := ret.Memory.Usage
2if v, ok := s.MemoryStats.Stats[inactiveFileKeyName]; ok {
3 if workingSet
在机器上直接 top 命令看到的值和 kubectl top node 不能直接对比,因为计算逻辑不同,如内存,大致的对应关系是(前者是机器上 top,后者是 kubectl top):
1rss + cache = (in)active_anon + (in)active_file
2
35.5 usage_in_bytes
4
5For efficiency, as other kernel components, memory cgroup uses some optimization
6to avoid unnecessary cacheline false sharing. usage_in_bytes is affected by the
7method and doesn't show 'exact' value of memory (and swap) usage, it's a fuzz
8value for efficient access. (Of course, when necessary, it's synchronized.)
9If you want to know more exact memory usage, you should use RSS+CACHE(+SWAP)
10value in memory.stat(see 5.2).
4.4 kubectl top pod 和 exec 进入 pod 后看到的 top 不一样
top 命令的差异和上边一致,无法直接对比,同时,就算你对 pod 做了 limit 限制,pod 内的 top 看到的内存和 cpu 总量仍然是机器总量,并不是pod 可分配量
- 进程的RSS为进程使用的所有物理内存(file_rss+anon_rss),即Anonymous pages+Mapped apges(包含共享内存)
- cgroup RSS为(anonymous and swap cache memory),不包含共享内存。两者都不包含file cache
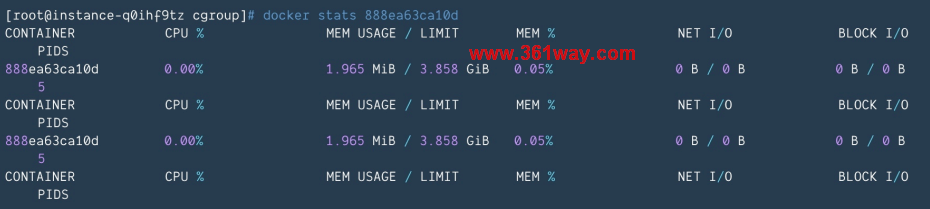
4.5 kubectl top pod 和 docker stats得到的值为什么不同?
docker stats dockerID 可以看到容器当前的使用量:
如果你的 pod 中只有一个 container,你会发现 docker stats 值不等于kubectl top 的值,既不等于 container_memory_usage_bytes,也不等于container_memory_working_set_bytes。因为docker stats 和 cadvisor 的计算方式不同,总体值会小于 kubectl top:计算逻辑是:
1docker stats = container_memory_usage_bytes - container_memory_cache
五、后记
一般情况下,我们并不需要时刻关心 node 或 pod 的使用量,因为有集群自动扩缩容(cluster-autoscaler)和 pod 水平扩缩容(HPA)来应对这两种资源变化,资源指标的意义更适合使用 prometheus 来持久化 cadvisor 的数据,用于回溯历史或者发送报警。其他补充:
- 虽然 kubectl top help 中显示支持 Storage,但直到 1.16 版本仍然不支持
- 1.13 之前需要 heapster,1.13 以后需要 metric-server,这部分 kubectl top help 的输出 有误,里面只提到了heapster
- k8s dashboard 中的监控图默认使用的是 heapster,切换为 metric-server后数据会异常,需要多部署一个metric-server-scraper 的 pod 来做接口转换,具体参考 pr:https://github.com/kubernetes/dashboard/pull/3504
注:本篇内容来自于网络内容摘取,部分内容基于测试进行了修改(发现多为转载,未能确认原出处,本处未标记原出处)
捐赠本站(Donate)
 如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))
如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))
- Author: shisekong
- Link: https://blog.361way.com/k8s-kubectl-top/6897.html
- License: This work is under a 知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议. Kindly fulfill the requirements of the aforementioned License when adapting or creating a derivative of this work.