linux IO工具iopp
linux下的IO检测工具之前最常用的是iostat ,不过iostat查看到的总的IO情况。如果要细看具体那一个程序点用的IO较高,可以使用iotop 。不过iotop 对内核版本和Python版本有要求,虽然目前主流的centos和ubuntu版本上都适用。不过考虑到其无法适用的场景,再推荐个可可以查看程序IO使用情况的工具iopp ---一个基于C语言开发的工具。
iopp非常mini ,源代码如下:
1#include <stdio.h>
2#include <sys/types.h>
3#include <dirent.h>
4#include <ctype.h>
5#include <sys/stat.h>
6#include <fcntl.h>
7#include <unistd.h>
8#include <string.h>
9#include <stdlib.h>
10#include <getopt.h>
11#define PROC "/proc"
12#define GET_VALUE(v)
13 p = strchr(p, ':');
14 ++p;
15 ++p;
16 q = strchr(p, 'n');
17 length = q - p;
18 if (length >= BUFFERLEN)
19 {
20 printf("ERROR - value is larger than the buffer: %dn", __LINE__);
21 exit(1);
22 }
23 strncpy(value, p, length);
24 value[length] = '';
25 v = atoll(value);
26#define BTOKB(b) b >> 10
27#define BTOMB(b) b >> 20
28#define BUFFERLEN 255
29#define COMMANDLEN 1024
30#define VALUELEN 63
31#define NUM_STRINGS 8
32struct io_node
33{
34 int pid;
35 long long rchar;
36 long long wchar;
37 long long syscr;
38 long long syscw;
39 long long read_bytes;
40 long long write_bytes;
41 long long cancelled_write_bytes;
42 char command[COMMANDLEN + 1];
43 struct io_node *next;
44};
45struct io_node *head = NULL;
46int command_flag = 0;
47int idle_flag = 0;
48int mb_flag = 0;
49int kb_flag = 0;
50int hr_flag = 0;
51/* Prototypes */
52char *format_b(long long);
53struct io_node *get_ion(int);
54struct io_node *new_ion(char *);
55void upsert_data(struct io_node *);
56char *
57format_b(long long amt)
58{
59 static char retarray[NUM_STRINGS][16];
60 static int index = 0;
61 register char *ret;
62 register char tag = 'B';
63 ret = retarray[index];
64 index = (index + 1) % NUM_STRINGS;
65 if (amt >= 10000) {
66 amt = (amt + 512) / 1024;
67 tag = 'K';
68 if (amt >= 10000) {
69 amt = (amt + 512) / 1024;
70 tag = 'B';
71 if (amt >= 10000) {
72 amt = (amt + 512) / 1024;
73 tag = 'G';
74 }
75 }
76 }
77 snprintf(ret, sizeof(retarray[index]) - 1, "%lld%c", amt, tag);
78 return (ret);
79}
80int
81get_cmdline(struct io_node *ion)
82{
83 int fd;
84 int length;
85 char filename[BUFFERLEN + 1];
86 char buffer[COMMANDLEN + 1];
87 char *p;
88 char *q;
89 length = snprintf(filename, BUFFERLEN, "%s/%d/cmdline", PROC, ion->pid);
90 if (length == BUFFERLEN)
91 printf("WARNING - filename length may be too big for buffer: %dn",
92 __LINE__);
93 fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
94 if (fd == -1)
95 return 1;
96 length = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
97 close(fd);
98 buffer[length] = '';
99 if (length == 0)
100 return 2;
101 if (command_flag == 0)
102 {
103 /*
104 * The command is near the beginning; we don't need to be able to
105 * the entire stat file.
106 */
107 p = strchr(buffer, '(');
108 ++p;
109 q = strchr(p, ')');
110 length = q - p;
111 }
112 else
113 p = buffer;
114 length = length < COMMANDLEN ? length : COMMANDLEN;
115 strncpy(ion->command, p, length);
116 ion->command[length] = '';
117 return 0;
118}
119struct io_node *
120get_ion(int pid)
121{
122 struct io_node *c = head;
123 while (c != NULL)
124 {
125 if (c->pid == pid)
126 break;
127 c = c->next;
128 }
129 return c;
130}
131int
132get_tcomm(struct io_node *ion)
133{
134 int fd;
135 int length;
136 char filename[BUFFERLEN + 1];
137 char buffer[BUFFERLEN + 1];
138 char *p;
139 char *q;
140 length = snprintf(filename, BUFFERLEN, "%s/%d/stat", PROC, ion->pid);
141 if (length == BUFFERLEN)
142 printf("WARNING - filename length may be too big for buffer: %dn",
143 __LINE__);
144 fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
145 if (fd == -1)
146 return 1;
147 length = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
148 close(fd);
149 /*
150 * The command is near the beginning; we don't need to be able to
151 * the entire stat file.
152 */
153 p = strchr(buffer, '(');
154 ++p;
155 q = strchr(p, ')');
156 length = q - p;
157 length = length < BUFFERLEN ? length : BUFFERLEN;
158 strncpy(ion->command, p, length);
159 ion->command[length] = '';
160 return 0;
161}
162struct io_node *
163insert_ion(struct io_node *ion)
164{
165 struct io_node *c;
166 struct io_node *p;
167 /* Check the head of the list as a special case. */
168 if (ion->pid < head->pid)
169 {
170 ion->next = head;
171 head = ion;
172 return head;
173 }
174 c = head->next;
175 p = head;
176 while (c != NULL)
177 {
178 if (ion->pid < c->pid)
179 {
180 ion->next = c;
181 p->next = ion;
182 return head;
183 }
184 p = c;
185 c = c->next;
186 }
187 /* Append to the end of the list. */
188 if (c == NULL)
189 p->next = ion;
190 return head;
191}
192void
193get_stats()
194{
195 DIR *dir = opendir(PROC);
196 struct dirent *ent;
197 char filename[BUFFERLEN + 1];
198 char buffer[BUFFERLEN + 1];
199 char value[BUFFERLEN + 1];
200 /* Display column headers. */
201 if (hr_flag == 1)
202 printf("%5s %5s %5s %8s %8s %5s %6s %7s %sn", "pid", "rchar", "wchar",
203 "syscr", "syscw", "reads", "writes", "cwrites", "command");
204 else if (kb_flag == 1)
205 printf("%5s %8s %8s %8s %8s %8s %8s %8s %sn", "pid", "rchar", "wchar",
206 "syscr", "syscw", "rkb", "wkb", "cwkb", "command");
207 else if (mb_flag == 1)
208 printf("%5s %8s %8s %8s %8s %8s %8s %8s %sn", "pid", "rchar", "wchar",
209 "syscr", "syscw", "rmb", "wmb", "cwmb", "command");
210 else
211 printf("%5s %8s %8s %8s %8s %8s %8s %8s %sn", "pid", "rchar", "wchar",
212 "syscr", "syscw", "rbytes", "wbytes", "cwbytes", "command");
213 /* Loop through the process table and display a line per pid. */
214 while ((ent = readdir(dir)) != NULL)
215 {
216 int rc;
217 int fd;
218 int length;
219 char *p;
220 char *q;
221 struct io_node *ion;
222 struct io_node *old_ion;
223 long long rchar;
224 long long wchar;
225 long long syscr;
226 long long syscw;
227 long long read_bytes;
228 long long write_bytes;
229 long long cancelled_write_bytes;
230 if (!isdigit(ent->d_name[0]))
231 continue;
232 ion = new_ion(ent->d_name);
233 if (command_flag == 1)
234 rc = get_cmdline(ion);
235 if (command_flag == 0 || rc != 0)
236 /* If the full command line is not asked for or is empty... */
237 rc = get_tcomm(ion);
238 if (rc != 0)
239 {
240 free(ion);
241 continue;
242 }
243 /* Read 'io' file. */
244 length = snprintf(filename, BUFFERLEN, "%s/%s/io", PROC, ent->d_name);
245 if (length == BUFFERLEN)
246 printf("WARNING - filename length may be too big for buffer: %dn",
247 __LINE__);
248 fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
249 if (fd == -1)
250 {
251 free(ion);
252 continue;
253 }
254 length = read(fd, buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 1);
255 close(fd);
256 buffer[length] = '';
257 /* Parsing the io file data. */
258 p = buffer;
259 GET_VALUE(ion->rchar);
260 GET_VALUE(ion->wchar);
261 GET_VALUE(ion->syscr);
262 GET_VALUE(ion->syscw);
263 GET_VALUE(ion->read_bytes);
264 GET_VALUE(ion->write_bytes);
265 GET_VALUE(ion->cancelled_write_bytes);
266 old_ion = get_ion(ion->pid);
267 /* Display the pid's io data. */
268 if (old_ion != NULL)
269 {
270 rchar = ion->rchar - old_ion->rchar;
271 wchar = ion->wchar - old_ion->wchar;
272 syscr = ion->syscr - old_ion->syscr;
273 syscw = ion->syscw - old_ion->syscw;
274 read_bytes = ion->read_bytes - old_ion->read_bytes;
275 write_bytes = ion->write_bytes - old_ion->write_bytes;
276 cancelled_write_bytes = ion->cancelled_write_bytes -
277 old_ion->cancelled_write_bytes;
278 if (kb_flag == 1 && hr_flag == 0)
279 {
280 rchar = BTOKB(rchar);
281 wchar = BTOKB(wchar);
282 syscr = BTOKB(syscr);
283 syscw = BTOKB(syscw);
284 read_bytes = BTOKB(read_bytes);
285 write_bytes = BTOKB(write_bytes);
286 cancelled_write_bytes = BTOKB(cancelled_write_bytes);
287 }
288 else if (mb_flag == 1 && hr_flag == 0)
289 {
290 rchar = BTOMB(rchar);
291 wchar = BTOMB(wchar);
292 syscr = BTOMB(syscr);
293 syscw = BTOMB(syscw);
294 read_bytes = BTOMB(read_bytes);
295 write_bytes = BTOMB(write_bytes);
296 cancelled_write_bytes = BTOMB(cancelled_write_bytes);
297 }
298 if (!(idle_flag == 1 && rchar == 0 && wchar == 0 && syscr == 0 &&
299 syscw == 0 && read_bytes == 0 && write_bytes == 0 &&
300 cancelled_write_bytes == 0)) {
301 if (hr_flag == 0)
302 printf("%5d %8lld %8lld %8lld %8lld %8lld %8lld %8lld %sn",
303 ion->pid,
304 rchar,
305 wchar,
306 syscr,
307 syscw,
308 read_bytes,
309 write_bytes,
310 cancelled_write_bytes,
311 ion->command);
312 else
313 printf("%5d %5s %5s %8lld %8lld %5s %6s %7s %sn",
314 ion->pid,
315 format_b(rchar),
316 format_b(wchar),
317 syscr,
318 syscw,
319 format_b(read_bytes),
320 format_b(write_bytes),
321 format_b(cancelled_write_bytes),
322 ion->command);
323 }
324 }
325 else if (idle_flag != 1)
326 /*
327 * No previous data, show 0's instead of calculating negatives
328 * only if we are shoring idle processes.
329 */
330 printf("%5d %8d %8d %8d %8d %8d %8d %8d %sn",
331 ion->pid, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, ion->command);
332 upsert_data(ion);
333 }
334 closedir(dir);
335 return;
336}
337struct io_node *
338new_ion(char *pid)
339{
340 struct io_node *ion;
341 ion = (struct io_node *) malloc(sizeof(struct io_node));
342 bzero(ion, sizeof(struct io_node));
343 ion->pid = atoi(pid);
344 return ion;
345}
346void
347upsert_data(struct io_node *ion)
348{
349 struct io_node *n;
350 /* List is empty. */
351 if (head == NULL)
352 {
353 head = ion;
354 return;
355 }
356 /* Check if we have seen this pid before. */
357 n = head;
358 while (n != NULL)
359 {
360 if (n->pid == ion->pid)
361 {
362 n->rchar = ion->rchar;
363 n->wchar = ion->wchar;
364 n->syscr = ion->syscr;
365 n->syscw = ion->syscw;
366 n->read_bytes = ion->read_bytes;
367 n->write_bytes = ion->write_bytes;
368 n->cancelled_write_bytes = ion->cancelled_write_bytes;
369 /*
370 * If the pids wrap, then the command may be different then before.
371 */
372 strcpy(n->command, ion->command);
373 free(ion);
374 return;
375 }
376 n = n->next;
377 }
378 /* Add this pid to the list. */
379 head = insert_ion(ion);
380 return;
381}
382void
383usage()
384{
385 printf("usage: iopp -h|--helpn");
386 printf("usage: iopp [-ci] [-k|-m] [delay [count]]n");
387 printf(" -c, --command display full command linen");
388 printf(" -h, --help display helpn");
389 printf(" -i, --idle hides idle processesn");
390 printf(" -k, --kilobytes display data in kilobytesn");
391 printf(" -m, --megabytes display data in megabytesn");
392 printf(" -u, --human-readable display data in kilo-, mega-, or giga-bytesn");
393}
394int
395main(int argc, char *argv[])
396{
397 int c;
398 int delay = 0;
399 int count = 0;
400 int max_count = 1;
401 while (1)
402 {
403 int option_index = 0;
404 static struct option long_options[] = {
405 { "command", no_argument, 0, 'c' },
406 { "help", no_argument, 0, 'h' },
407 { "human-readable", no_argument, 0, 'u' },
408 { "idle", no_argument, 0, 'i' },
409 { "kilobytes", no_argument, 0, 'k' },
410 { "megabytes", no_argument, 0, 'm' },
411 { 0, 0, 0, 0 }
412 };
413 c = getopt_long(argc, argv, "chikmu", long_options, &option_index);
414 if (c == -1)
415 {
416 /* Handle delay and count arguments. */
417 if (argc == optind)
418 break; /* No additional arguments. */
419 else if ((argc - optind) == 1)
420 {
421 delay = atoi(argv[optind]);
422 max_count = -1;
423 }
424 else if ((argc - optind) == 2)
425 {
426 delay = atoi(argv[optind]);
427 max_count = atoi(argv[optind + 1]);
428 }
429 else
430 {
431 /* Too many additional arguments. */
432 usage();
433 return 3;
434 }
435 break;
436 }
437 switch (c)
438 {
439 case 'c':
440 command_flag = 1;
441 break;
442 case 'h':
443 usage();
444 return 0;
445 case 'i':
446 idle_flag = 1;
447 break;
448 case 'k':
449 kb_flag = 1;
450 break;
451 case 'm':
452 mb_flag = 1;
453 break;
454 case 'u':
455 hr_flag = 1;
456 break;
457 default:
458 usage();
459 return 2;
460 }
461 }
462 while (max_count == -1 || count++ < max_count)
463 {
464 get_stats();
465 if (count != max_count)
466 sleep(delay);
467 }
468 return 0;
469}
将以上代码保存为iopp.c ,执行gcc -o iopp iopp.c 编译出可执行文件iopp 。具体用法可以使用./iopp -h查看,如果查出将结果输出到文件,可以执行类似如下的命令:
1./iopp -i -k -c 1 > io.log
执行时具体各项指示的含义如下:
- pid 进程ID
- rchar 将要从磁盘读取的字节数
- wchar 已经写入或应该要写入磁盘的字节数
- syscr 读I/O数
- syscw 写I/O数
- rbytes 真正从磁盘读取的字节数
- wbytes 真正写入到磁盘的字节数
- cwbytes 因为清空页面缓存而导致没有发生操作的字节数
- command 执行的命令
2016-01-07后记:
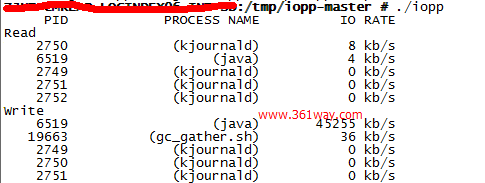
iopp的实现原理非常简单,无非是遍历/proc/pid/io文件,读取出结果后,再通过进一步计算得出。大部分时候,我们只关注参数rbytes和wbytes两部分,上面贴的该版本的iopp在实际应用中很多时候并不尽人意,所以后续也有人出了基于c++优化的一个iopp,c++版本的输出结果如下图:
输出结果是时时刷新的,比iotop轻量级。
C 语言iopp github地址:https://github.com/markwkm/iopp
C++ 版iopp github地址:https://github.com/hackerforward/iopp
捐赠本站(Donate)
 如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))
如您感觉文章有用,可扫码捐赠本站!(If the article useful, you can scan the QR code to donate))
- Author: shisekong
- Link: https://blog.361way.com/linux-iopp/3583.html
- License: This work is under a 知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议. Kindly fulfill the requirements of the aforementioned License when adapting or creating a derivative of this work.